Recreational Cannabis Shop
Portland, Maine


NEW DROPS
DAILY DISPENSARY DEALS


367 Fore Street
Portland, Maine
21+ Adult-use, recreational dispensary located in the heart of the historic Old Port District of Portland, Maine

100% LOCAL & INDEPENDENT
Since our inception in 2018, our goal is to curate a truly unique dispensary experience with THC & CBD products that exemplify the highest standards of quality. We are committed to working with local, independent growers, concentrate producers, & edible makers that are dedicated to enriching Maine’s cannabis community and creating clean cannabis products. As the first medical dispensary in Portland’s Old Port, we opened our doors in 2019, proudly serving the Maine Medical Marijuana Community for 4 years & strongly support the continuation of the MMCP/MMMP. With our extensive industry knowledge, we led the charge & reopened as the first Adult Use/21+ Recreational Cannabis Dispensary in the Old Port of Portland, ME in 2022.
FEATURING
Our roots run deep at Firefly Organics. We are Maine owned and operated constantly evolving and striving for the best. Providing a quality product that expresses a superior taste, nose and effectiveness. Our focus is maintaining the quality and consistency that our customers have come to expect.
We cultivate in soil, hand-mix organic nutrients, and focus on daily interactions in our facility that allows the plant to tell us its needs.. This practice establishes the foundation each strain needs to meet our Firefly Organics standard of quality and consistency. All of our strains are hand trimmed, cured and stored in climate controlled rooms. Producing a consistent quality assured product. We are continuing our partnership with BioBizz which has maintained a 25 year, 100% organic plant nutrient presence in the cannabis sector worldwide. We believe that these cultivation practices give our plants and products the best terpene expression and highest quality flower to the end consumer.
“Cultivated with love by smokers for smokers.”
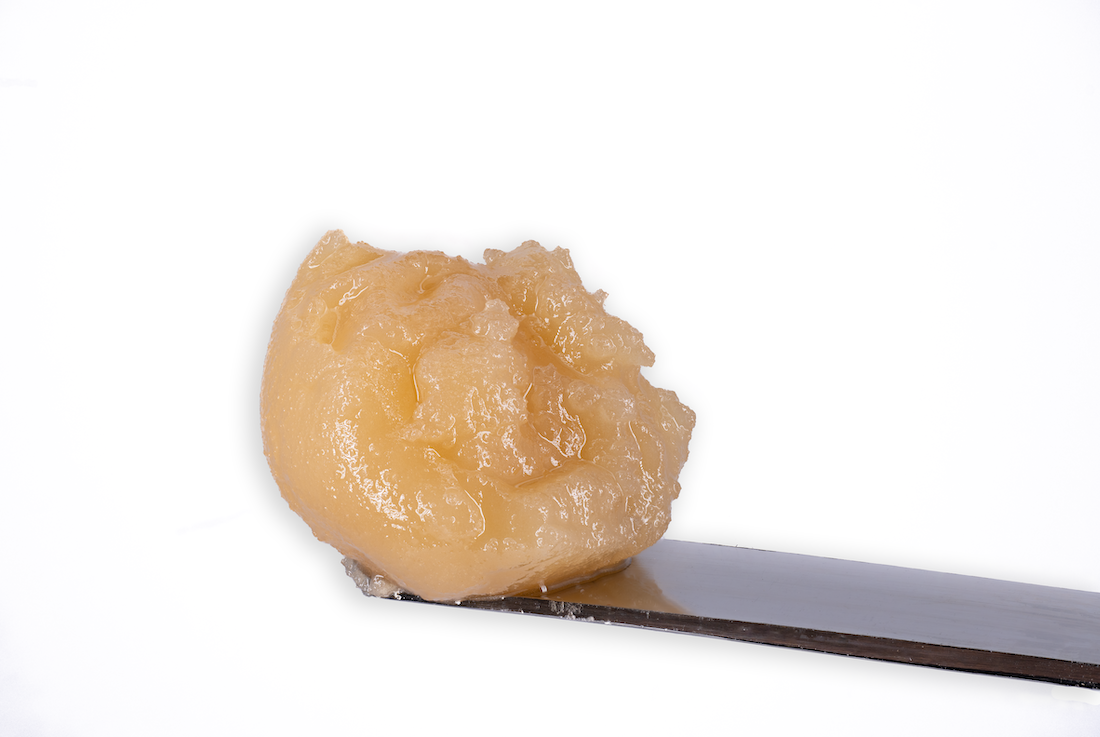
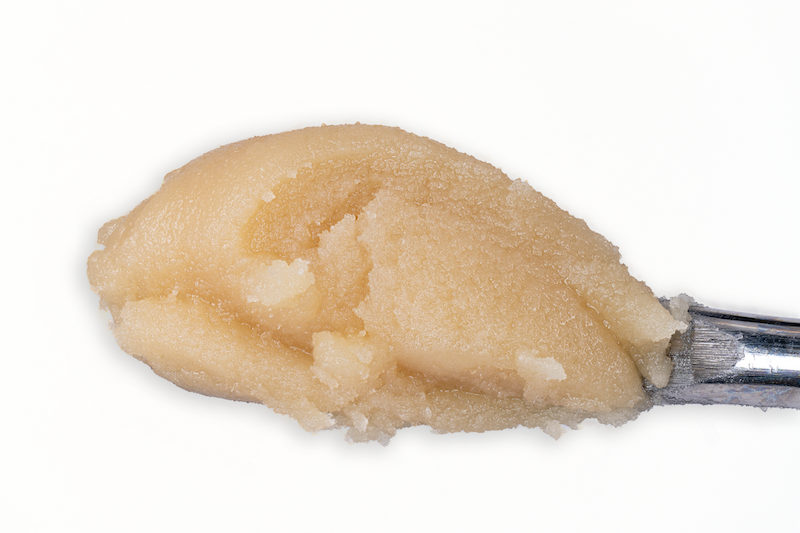
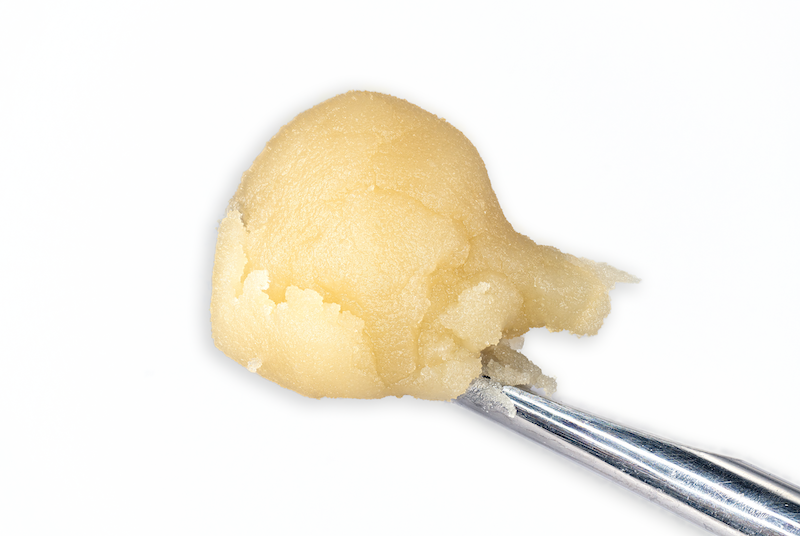
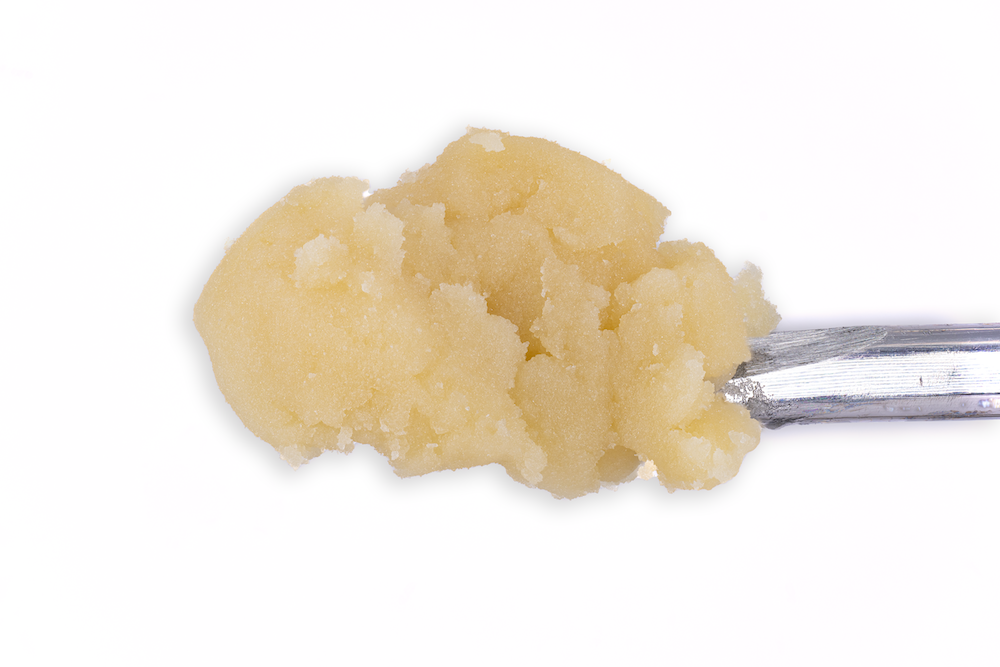
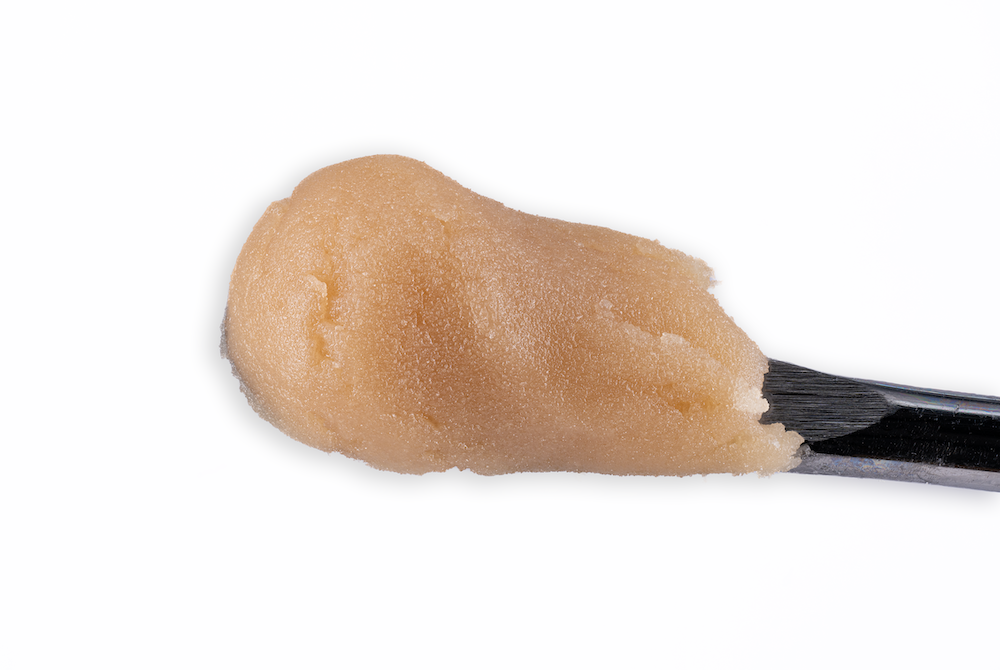
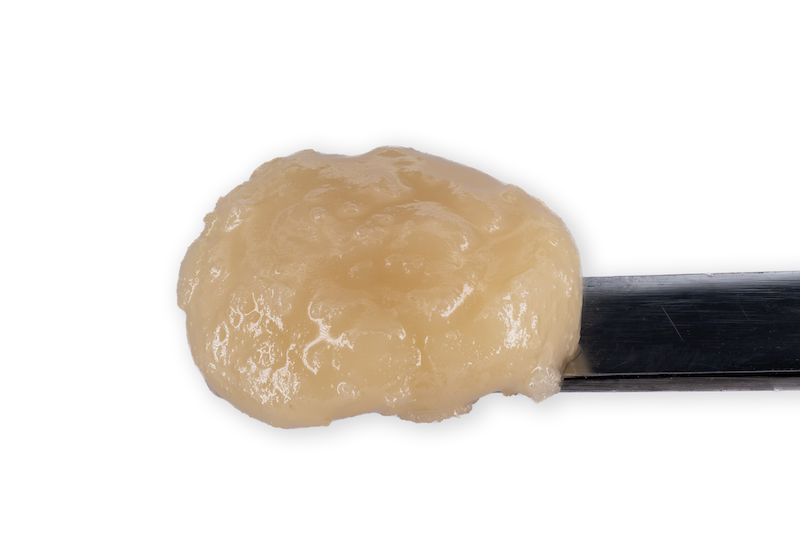
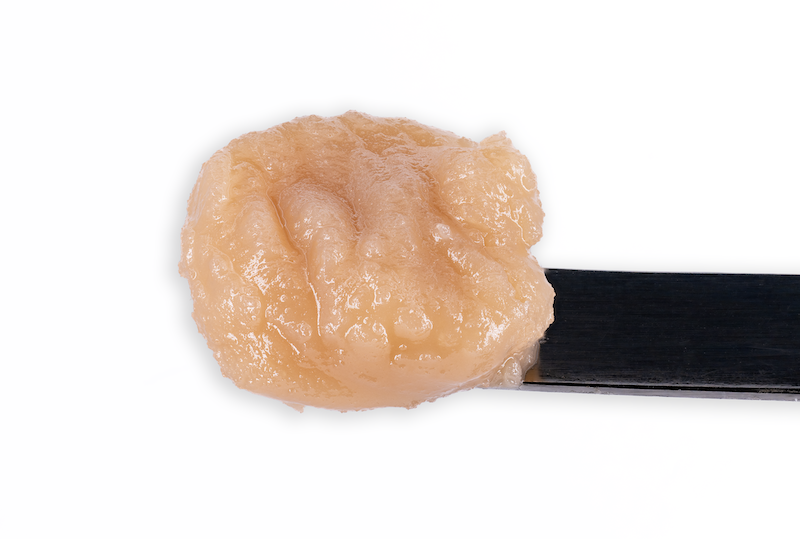
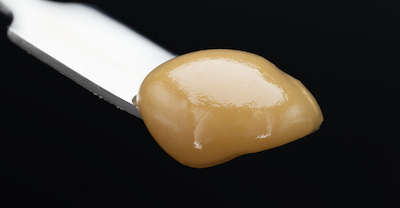
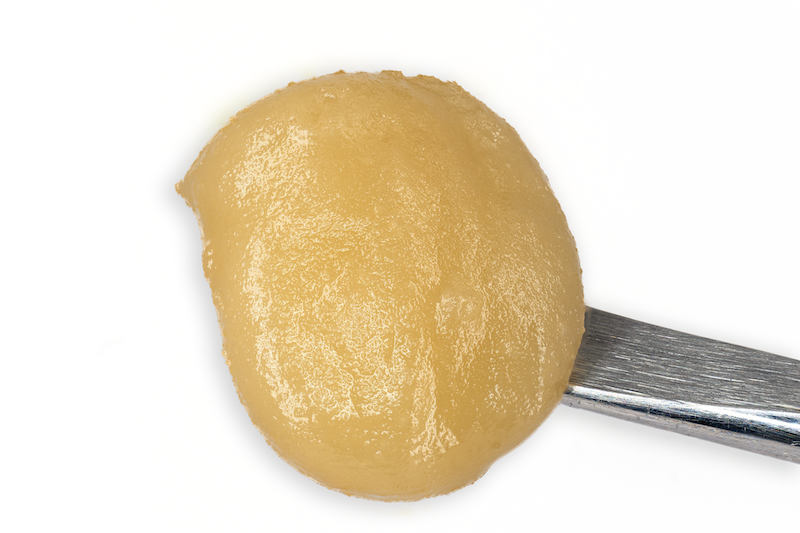
Cold Cure HASH ROSIN
Processed by
HELIOS HASH
“Two maestros of Cannabis cultivation, Helios Collective and FireFly Organics, have orchestrated a new duet with… hash rosin that’s a crescendo of flavor and experience…
Grown By
FIREFLY ORGANICS
…In the ever-evolving landscape of Cannabis, collaborations often spark innovation and when these two join forces, it’s not just a partnership … it’s a symphony of cultivation and extraction expertise.”
-Leaf Magazine

-
The cannabis plant has several important parts, each serving a distinct purpose and containing different compounds of interest. Here are some key parts of the cannabis plant:
Flowers/Buds: The flowers, also known as buds, are the reproductive organs of the female cannabis plant. They are the most coveted part of the plant as they contain the highest concentrations of cannabinoids, such as THC and CBD, as well as terpenes. The flowers are typically harvested and dried for consumption or further processing into various cannabis products.
Leaves: Cannabis leaves are usually characterized by their serrated edges and can vary in size and shape depending on the strain. While they contain lower concentrations of cannabinoids and terpenes compared to the flowers, they still contain some beneficial compounds. Leaves are often trimmed away from the buds before consumption or processing, although they can be used to make teas or extracts.
Stems: Stems are the main structural components of the cannabis plant, providing support and transporting water, nutrients, and sugars throughout the plant. They are typically less sought after for their cannabinoid content and are often discarded or used for fiber production in industrial hemp.
Seeds: Cannabis seeds are the reproductive units of the plant and are primarily used for propagation purposes. They are a rich source of essential fatty acids, proteins, and other nutrients. Cannabis seeds can be consumed as food, sprouted for gardening, or pressed for their oil, which is used in various culinary and cosmetic applications.
Trichomes: Trichomes are tiny, hair-like structures that cover the flowers, leaves, and sometimes even stems of the cannabis plant. They contain the majority of the plant's cannabinoids, terpenes, and other compounds of interest. Trichomes give cannabis its resinous texture and contribute to the plant's aromatic and therapeutic properties.
It's worth noting that the concentration and composition of cannabinoids and terpenes can vary among different parts of the cannabis plant. The flowers/buds, with their high cannabinoid content, are typically the most valuable and sought-after part, but other parts of the plant also have their uses in various applications, such as fiber production, seed-based products, or extractions.
-
In cannabis, terpenes are organic compounds that contribute to the plant's distinct aroma and flavor profile. They are secreted in the resin glands of the cannabis flowers, along with cannabinoids such as THC (tetrahydrocannabinol) and CBD (cannabidiol).
Terpenes in cannabis serve several important purposes:
Aroma and Flavor: Terpenes are responsible for the wide range of fragrances found in different cannabis strains, such as citrus, pine, berry, or earthy scents. These aromatic compounds also contribute to the unique flavors experienced when consuming cannabis.
Entourage Effect: Terpenes interact synergistically with cannabinoids, enhancing or modulating their effects in what is known as the entourage effect. Different combinations of terpenes and cannabinoids can produce varying physiological and psychological responses. For example, some terpenes may promote relaxation, while others may have uplifting or energizing effects.
Therapeutic Potential: Terpenes have been found to possess potential therapeutic properties on their own. For instance, some terpenes have demonstrated anti-inflammatory, analgesic, anxiolytic (anxiety-reducing), or sedative properties. When combined with cannabinoids, these terpenes may contribute to the overall therapeutic potential of cannabis.
Differentiation of Strains: Terpene profiles can help differentiate cannabis strains and guide consumers in selecting strains that suit their preferences or desired effects. For example, strains high in the terpene myrcene may be associated with relaxation, while strains high in limonene may be more uplifting.
It's important to note that terpenes are not exclusive to cannabis and can be found in various plants. However, they play a significant role in the overall cannabis experience, influencing both the sensory aspects and potential therapeutic effects of the plant.
There are numerous terpenes found in cannabis, but here are some of the primary terpenes commonly identified in cannabis strains:
Myrcene: This is one of the most abundant terpenes in cannabis. It has an earthy, musky aroma and is also found in hops. Myrcene is associated with sedative effects and is believed to contribute to the "couch-lock" sensation.
Limonene: As the name suggests, limonene has a citrusy, lemon-like scent. It is also found in various citrus fruits. Limonene is associated with uplifting and mood-enhancing effects and may have potential anti-anxiety and anti-depressant properties.
Pinene: Pinene has a distinctive pine aroma and is found in pine trees, as well as some herbs. It is believed to have anti-inflammatory properties and may help with focus and alertness. There are two types of pinene: alpha-pinene and beta-pinene.
Caryophyllene: Caryophyllene has a spicy, peppery scent and is also found in black pepper, cloves, and other spices. It binds to the cannabinoid receptors in the body, making it unique among terpenes. Caryophyllene is associated with anti-inflammatory and analgesic effects.
Linalool: Linalool has a floral, lavender-like aroma and is found in lavender, as well as other flowers and spices. It is believed to have relaxing and sedative properties and may help with anxiety and stress relief.
Humulene: Humulene has an earthy, woody aroma and is also found in hops. It is associated with anti-inflammatory effects and may have appetite-suppressing properties.
These are just a few examples, and there are many more terpenes present in cannabis, each with its own unique scent and potential effects. The combination and concentration of terpenes in a particular cannabis strain contribute to its specific aroma, flavor, and potential therapeutic effects.
-
Cannabinoids are a group of chemical compounds that are naturally found in cannabis plants. They interact with the endocannabinoid system (ECS) in the human body and have various effects on physiological processes. Over 100 different cannabinoids have been identified in cannabis, with the most well-known and studied ones being THC (tetrahydrocannabinol) and CBD (cannabidiol).
Here are some key cannabinoids found in cannabis:
THC (tetrahydrocannabinol): THC is the primary psychoactive compound in cannabis, responsible for the "high" or euphoric effects. It binds to cannabinoid receptors in the brain and central nervous system, producing various psychoactive and physiological effects. THC is also known for its potential analgesic (pain-relieving) and anti-nausea properties.
CBD (cannabidiol): CBD is another major cannabinoid found in cannabis. Unlike THC, CBD is not psychoactive, meaning it doesn't produce a euphoric high. However, it has gained significant attention for its potential therapeutic properties, such as anti-inflammatory, analgesic, anxiolytic (anxiety-reducing), and anticonvulsant effects. CBD can also modulate the effects of THC.
CBG (cannabigerol): CBG is considered a minor cannabinoid as it is typically found in lower concentrations in cannabis plants. It has been studied for its potential anti-inflammatory, antibacterial, and neuroprotective properties. CBG is also known as the precursor to other cannabinoids, as enzymes in the plant convert CBG into THC, CBD, and other cannabinoids during the growth process.
CBC (cannabichromene): CBC is a non-psychoactive cannabinoid that is being investigated for its potential anti-inflammatory, analgesic, and antidepressant properties. It may also have synergistic effects with other cannabinoids, enhancing their overall therapeutic potential.
CBN (cannabinol): CBN is a mildly psychoactive cannabinoid that is formed when THC degrades over time. It is known for its potential sedative effects and is sometimes associated with a more relaxing experience.
These are just a few examples of the cannabinoids found in cannabis. Each cannabinoid interacts with the body's endocannabinoid system in different ways, leading to various effects. The combination and ratios of cannabinoids in a cannabis strain can influence its overall effects and potential therapeutic benefits.
-
The process of extracting key components from cannabis plant material, such as oils, cannabinoids, and terpenes, involves a variety of methods that can be broadly categorized into solvent-based and solventless techniques. Each method has its own set of advantages and is chosen based on the desired outcome, efficiency, safety, and purity of the final product.
Solventless Extraction
Solventless extraction methods do not use chemical solvents. Instead, they rely on physical means such as heat, pressure, or filtration to extract the desired components from the cannabis plant. One popular solventless method is ROSIN extraction. This technique involves pressing dried flower, kief, dry sift, or bubble hash between two heated plates. The temperatures typically range from 120°F to 220°F. The combination of high pressure and controlled heat allows for the extraction of highly potent concentrates, with THC levels reaching up to 90%, while preserving the terpene profile, aroma, and flavor of the original plant material.
Solvent-based Extraction
In contrast, solvent-based extraction methods use chemical solvents such as butane, propane, and ethanol to dissolve the plant material and extract the desired compounds. This method is considered more efficient in extracting trichomes from the plant material but requires careful attention to safety due to the flammable nature of the solvents used. It also necessitates a thorough post-extraction process to remove any residual solvents from the final product, ensuring it is safe for consumption.
Hydrocarbon or Ethanol Extraction: These are common solvent-based techniques. Extracts made with butane as the primary solvent are known as Butane Hash Oil (BHO). These methods are highly efficient but require rigorous safety measures.
LIVE Products: This is a specific type of concentrate produced by freezing the flower immediately after harvest and keeping the material frozen throughout the extraction process. This technique, which can be applied in solvent-based extractions, is designed to preserve the terpene profile, cannabinoids, and flavonoids of the plant material as effectively as possible.
CURED Products: These are created from dried and cured plant material, in contrast to live resin. The drying and curing process can affect the terpene profile and overall flavor of the final product.
Both solvent-based and solventless extraction methods offer unique advantages and cater to different preferences in the cannabis community. Solventless methods are often praised for their ability to preserve the natural qualities of the cannabis plant without the use of chemicals, making them a popular choice for consumers seeking a more "natural" product. On the other hand, solvent-based extractions are valued for their efficiency and the ability to produce highly potent concentrates. Safety, purity, and the preservation of the plant's original characteristics are key considerations in choosing the appropriate extraction method.
-
Importance of Trichomes:
Trichomes produce cannabinoids like THC and CBD, which are responsible for the plant's psychoactive and therapeutic effects. They also produce terpenes, which contribute to the plant's aroma and flavor, and can influence its effects and therapeutic potential. Trichomes serve as a defense mechanism against pests, UV radiation, and environmental stressors by secreting a resinous substance that acts as a deterrent.
Peak Timing:
The peak period is often indicated by the color of the trichomes. They start clear, turn milky or cloudy as they mature, and eventually become amber. Harvesting is usually timed when trichomes are mostly milky with some amber, as this stage is believed to offer optimal potency and effects.
Effects on Users:
The concentration of cannabinoids and terpenes in trichomes directly affects the potency and the specific effects of the cannabis strain. High trichome density generally means more potent and flavorful cannabis. The maturity and composition of trichomes influence the psychoactive effects experienced by users. Terpenes and cannabinoids from trichomes work together to produce the plant’s therapeutic effects. The presence of specific terpenes can modulate the impact of cannabinoids, affecting things like relaxation, pain relief, or mood enhancement.